Understanding the Importance and Construction of Retaining Walls
Introduction to Retaining Walls
Retaining walls are essential structures in both residential and commercial landscapes. They serve the primary function of holding back soil and preventing erosion, which is particularly crucial in areas with significant elevation changes. By providing structural support, retaining walls enable the creation of level spaces on sloped terrains, facilitating the construction of gardens, patios, and driveways. Their importance cannot be overstated, as they contribute significantly to the stability and aesthetics of a property.
These walls are not only functional but also contribute to the visual appeal of a landscape. They can be constructed from various materials, including stone, concrete, and wood, each offering unique benefits and aesthetic qualities. Understanding the different types of retaining walls and their specific applications is vital for anyone involved in landscape design or construction.
Types of Retaining Walls
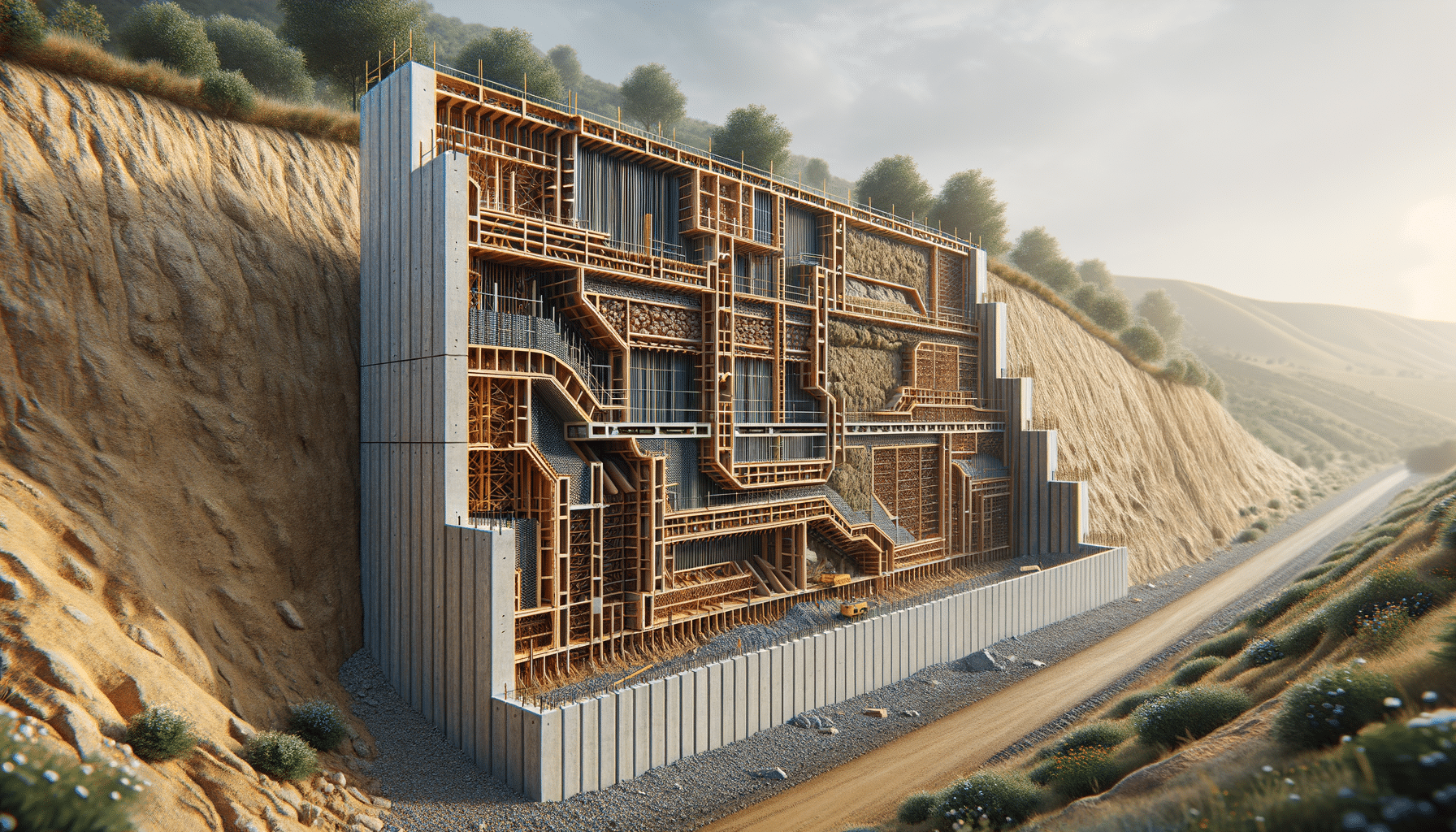
There are several types of retaining walls, each designed to meet specific needs and conditions. The most common types include gravity walls, cantilever walls, and anchored walls.
- Gravity Walls: These rely on their mass to resist the pressure of the soil behind them. They are typically constructed from heavy materials like stone or concrete.
- Cantilever Walls: These are reinforced with steel bars and use a lever arm to hold back the soil. They are more complex to build but can support taller structures.
- Anchored Walls: These use cables or other supports anchored into the rock or soil behind the wall, providing additional stability.
Choosing the right type of retaining wall depends on factors such as soil type, the slope of the terrain, and the intended use of the area. A well-designed retaining wall not only performs its functional role but also enhances the landscape’s beauty.
Materials Used in Retaining Wall Construction
The choice of materials for constructing a retaining wall is crucial, as it affects both the wall’s durability and aesthetic appeal. Common materials include:
- Concrete: Known for its strength and versatility, concrete can be molded into various shapes and styles, making it a popular choice for modern landscapes.
- Stone: Offering a natural look, stone is ideal for creating rustic and traditional landscapes. It’s highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Wood: While not as durable as stone or concrete, wood provides a warm, natural appearance. It is best used in smaller, residential projects where aesthetics are a priority.
The selection of materials should consider factors such as climate, budget, and personal preference. Each material offers distinct advantages, and the right choice can significantly impact the wall’s performance and appearance.
Design Considerations for Retaining Walls
Designing a retaining wall involves several considerations to ensure it is both functional and visually appealing. Key factors include:
- Height and Slope: The height of the wall and the slope of the terrain will determine the type of wall and materials needed.
- Drainage: Proper drainage is critical to prevent water buildup behind the wall, which can lead to structural failure.
- Soil Type: Different soils exert different pressures on a retaining wall, influencing the design and reinforcement requirements.
Incorporating these considerations into the design process helps create a retaining wall that is not only effective in its purpose but also complements the surrounding environment. Collaboration with experienced engineers and landscape architects can ensure the wall meets all necessary criteria.
Maintenance and Longevity of Retaining Walls
Like any structural element, retaining walls require regular maintenance to ensure their longevity and effectiveness. Key maintenance practices include:
- Inspection: Regular inspections help identify any signs of wear or damage, such as cracks or bulges, allowing for timely repairs.
- Cleaning: Removing debris and vegetation that can trap moisture and cause deterioration is essential for maintaining the wall’s integrity.
- Drainage Management: Ensuring that drainage systems remain clear and functional prevents water accumulation that can compromise the wall’s stability.
By adhering to these maintenance practices, property owners can extend the life of their retaining walls, ensuring they continue to perform their vital functions while enhancing the landscape’s appearance.


